Comedia Utils Overview
(version 1.1)
The project contains some general purpose pure java classes.
They do not require any special libraies.
Classes can be separated into several independent parts.
The static class diagram is presented below:
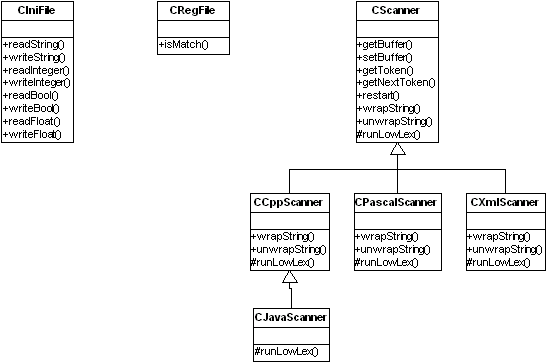
Windows INI-Files API
It emulates standard Windows INI-File interface. The class loads
and entire INI-File into RAM and performs all operations on
memory image. At the end of the work the image can then be written back
to disk file.
The class can use files from JARs or Web-sites addressed by URLs
but it can not flush them of cause.
Example of usage:
CIniFile iniFile = new CIniFile("test.ini");
boolean p1 = iniFile.readBool("Section 1", "P1", false);
System.out.println("P1 = " + p1);
iniFile.writeBool("Section 1", "P1", !p1);
System.out.println("Section 2, Parameter 1 = "
+ iniFile.readString("Other X", "Param1", ""));
System.out.println("Section 2, Parameter 2 = "
+ iniFile.readInteger("Section 2", "P2", 123));
System.out.println("Section 2, Parameter 3 = "
+ iniFile.readDateTime("Section 2", "P3", new Date()));
iniFile.writeString("Section 2", "P1", "..\"xxx\"...");
iniFile.writeDateTime("Section 2", "P3", new Date());
iniFile.flush();
Unix Grep Like Regular Expressions
This class implements regular expressions algorithms.
It allows unix grep-like pattern comparisons, for instance:
? - Matches any single characer
* - Matches any contiguous characters
[abc] - Matches a or b or c at that position
[^abc] - Matches anything but a or b or c at that position
[!abc] - Ditto
[a-e] - Matches a through e at that position
Usage examples:
System.out.println("The match result (1): "
+ CRegExp.isMatch("BLA", "BLA"));
System.out.println("The match result (2): "
+ CRegExp.isMatch("A*", "ABBA"));
System.out.println("The match result (3): "
+ CRegExp.isMatch("[A-Z,_]*[A-Z,0-9,_]*0?7*", "AGENT_007"));
Lexical Scanners
The scanner package contains classes which performs lexical
analisys (parsing) of input text. They receive a string buffer
split it into a set of lexem (or terminals).
Different languages are supported by descendant classes such as
C++, Pascal, Java, XML or others.
Lexical scanners supports several types of lexems:
COMMENT - Single line or multiline comments.
KEYWORD - Language specific keywords.
TYPE - Language specific standard data types.
IDENT - Identificators.
OPERATOR - Language specific operators: simple ('-', '=' or '%'),
or complex ('>=', '<=') or presented by keywords ('or', 'and').
BRACE - Different braces like '[]', '()' or '{}'.
SEPARATOR - Other delimiters (',', '.', ':' or ';').
EOL - New line character ('\n').
LN - Line feed character ('\r').
SPACE - String contanes white space characters (' ' or '\t').
INT - Integer constant.
FLOAT - Float constant.
STRING - String constant.
BOOL - Boolean constant.
EOF - End-Of-File symbol.
These scanners can be very useful in applications of different types
from editors with syntax highlighting to implementation of program
language compilers.
Example of simple scanner usage:
System.out.println("*********** Scanner Test *************");
CScanner scanner = new CScanner();
scanner.setBuffer("while(1.0e2*i := \t\r\n> \"string\'\'\")\n"
+ "// comment\n/.*second\ncomment*./{xxx}");
scanner.setShowEol(true);
scanner.setShowSpace(true);
// Testing string convertions
String str = "The test \"string\"";
System.out.println("Start string: " + str);
str = scanner.wrapString(str);
System.out.println("Wrapped string: " + str);
str = scanner.unwrapString(str);
System.out.println("Unwrapped string: " + str);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Initial string: " + scanner.getBuffer());
while (scanner.lex() != EOF) {
switch (scanner.getTokenType()) {
case UNKNOWN: System.out.print("Type: Unknown "); break;
case COMMENT: System.out.print("Type: Comment "); break;
case KEYWORD: System.out.print("Type: Keyword "); break;
case TYPE: System.out.print("Type: Type "); break;
case IDENT: System.out.print("Type: Ident "); break;
...
}
System.out.println("Value: '" + scanner.getToken()
+ "' Pos: " + scanner.getPosition() + " Line: " + scanner.getLineNo());
}
The result of this program could be the next:
*********** Scanner Test *************
Start string: The test "string"
Wrapped string: "The test "string""
Unwrapped string: The test "string"
Initial string: while(1.0e2*i :=
> "string''")
// comment
/.second
comment./{xxx}
Type: Ident Value: 'while' Pos: 0 Line: 0
Type: Brace Value: '(' Pos: 5 Line: 0
Type: Float Value: '1.0e2' Pos: 6 Line: 0
Type: Operator Value: '*' Pos: 11 Line: 0
Type: Ident Value: 'i' Pos: 12 Line: 0
...
Download
Download version 1.1...

